Table of Contents
Businesses across all industries are expanding digital transformation plans that rely heavily on the cloud. Cloud architectures enable enterprises to innovate and overcome risks, so on-demand self-service cloud environments justify cloud migration planning.
When migrating your digital assets to cloud infrastructure, you must be confident in the cloud migration process and the results. Too often, cloud platform computing efforts fail to produce the expected benefits. Sometimes the entire project stops, or apps underperform in the cloud to the point that they must be “repatriated,” or returned on-premises.
Read also: What is Meta App Manager & its Purpose
What Is a Cloud Migration Strategy?
A cloud migration strategy is a company’s plan to move its apps and data from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud. Before going live, confirming the most effective strategy to prioritize and move apps is crucial because not all workloads benefit from running on cloud-based infrastructure. It is essential to have a well-organized, written plan.
Successful Cloud Migration Strategies
Effective cloud migration strategy is hampered by the difficulties of untangling complicated, interwoven applications and a general lack of insight into the original computing environment. Nothing is neglecting the never-ending debates over cloud charges.
You have an insurance policy to evaluate and manage your risk by defining a baseline before your project and comparing it to the metrics recorded after the shift. You’ll also have clear metrics to determine whether your cloud implementation succeeded.
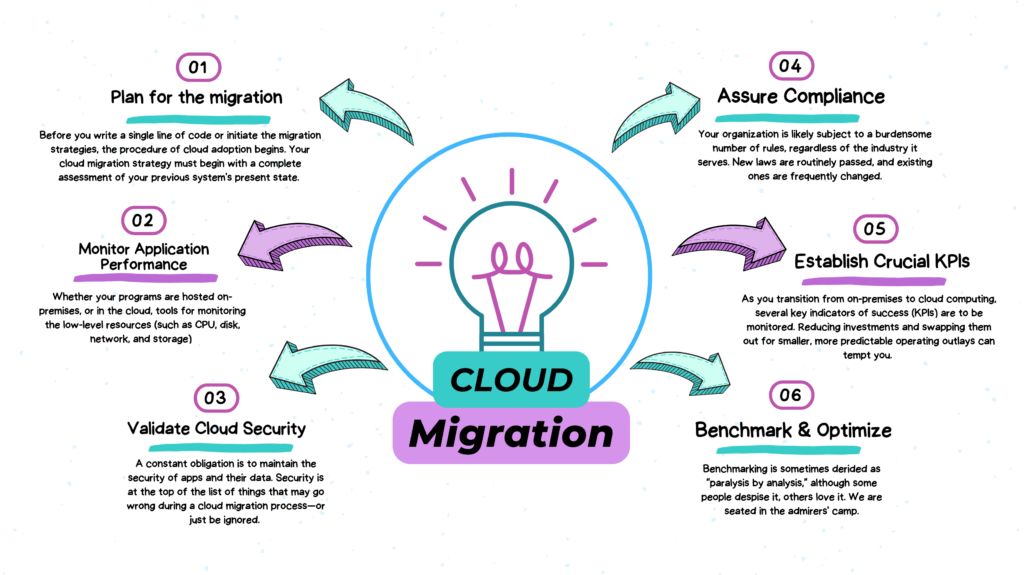
Plan for the migration
Before you write a single line of code or initiate the migration strategies, the procedure of cloud adoption begins. Your cloud migration strategy must begin with a complete assessment of your previous system’s present state. You can better understand the issue at hand by utilizing your existing infrastructure.
Pay attention to the massive volumes of everyday machine data you create due to your normal activities, as this data contains valuable insights that can aid in your migration planning. Evaluate your “before” image to compare it to your “after” image.
The machine data center provides a complete inventory of servers, applications, and supporting technologies. It demonstrates the relationships between microservices, apps, and users to correlate and display critical metrics with custom dashboards for full-stack visibility.
Monitor Application Performance
Whether your programs are hosted on-premises, or in the cloud, tools for monitoring the low-level resources (such as CPU, disk, network, and storage) that power them give you good insights into the health of your base legacy systems, but none on the state of your existing applications, their responsiveness, or whether there are errors.
You may gain a deeper understanding of the new state if you first acquire and examine this data while the infrastructure is configured as it is now and then after the cloud transfer. You can quickly determine excessive or insufficient provisioning in your new environment by fusing system-level resource observations with application performance monitoring.
Validate Cloud Security
A constant obligation is to maintain the security of apps and their data. Security is at the top of the list of things that may go wrong during a cloud migration process—or just be ignored. According to recent research, 81% of participants named cloud security the main obstacle to moving workloads to the cloud.
Machine data is crucial to secure your information-processing environment before, during, and after the transition to the cloud. Its analytics and machine learning skills can quickly process enormous amounts of raw log data to identify possible vulnerabilities.
Assure Compliance
Your organization is likely subject to a burdensome number of rules, regardless of the industry it serves. New laws are routinely passed, and existing ones are frequently changed. Serious consequences might result from not adhering to these regulations, including possible civil and criminal fines.
To secure your company, you must implement machine data-driven compliance baselines before the move. This approach indicates ongoing compliance, which will be beneficial in the next regulatory audits that are unavoidable.
Establish Crucial KPIs
As you transition from on-premises to cloud computing, several key indicators of success (KPIs) are to be monitored. Reducing investments and swapping them out for smaller, more predictable operating outlays can tempt you. Consider giving cloud capabilities’ versatility and scalability a priority.
The only method to determine whether your firm is living up to its promised potential, no matter what the essential statistic for your organization may be. It is to establish and then consistently assess KPIs, whether they are business- or technical-focused indicators.
Benchmark and Optimize
Benchmarking is sometimes derided as “paralysis by analysis,” although some people despise it, others love it. We are seated in the admirers’ camp. Population benchmarks add context to incidents, speed up troubleshooting, and serve as a symptom checker for determining the relative importance of errors.
To allow you to compare your company’s operational and security posture to that of other Sumo Logic clients, we generate benchmarks by adding crowdsourcing context to signals, such as failures noticed during an event. Anomalies found from an object’s historical baselines are validated and prioritized by cloud-native features like benchmark context.
Codify Monitoring Workflows
The premises data centers and streaming signals produced by your digital assets provide insightful contextual data on the actions of your users, stakeholders, and buyers. You may need real-time insights to stay competitive by observing and acting on this information with cloud technologies.
Simple procedures include:
- Adding information from other systems.
- Connecting it all.
- Creating a dashboard that provides a complete picture of your business case.
Sharing, treating as code, modifying, reviewing, and version-tracking procedures is possible by codifying them into declarative configuration files.
Ensure Data Portability & Interoperability
Until a few years ago, multi-cloud exclusively represented a corporate cloud strategy. The obvious first step for the majority was learning to do everything cloud-first. While continuing to use their outdated data centers and keeping an eye on the larger picture, businesses were managing workloads in a single cloud.
As a result of the multi-cloud strategy’s success, businesses now typically use a combination of three or more private and public cloud systems.
Businesses are increasingly utilizing the full economic potential of the cloud computing concept by running production workloads across several public clouds and cautiously implementing cloud services to guarantee workload portability and interoperability.
Make sure you effortlessly collect your data and translate it into real-time analytics and insights for unified visibility across your complex, contemporary application infrastructures if you intend on using a multi-cloud strategy.
It would help if you had a uniform data-gathering strategy to facilitate data portability and interoperability and avoid using several different migration strategies to get end-to-end visibility.
Benefits of Cloud Migration Strategy
The cloud may have a significant influence on businesses that go through the process of cloud migration.
It entails lower total cost of ownership (TCO), quicker delivery, and better prospects for innovation. Agility and flexibility are essential for meeting shifting customer and industry expectations, and access to the cloud brings them both.
Businesses have moved their services and data to the cloud in recent months, transforming into flexible digital migrating workloads to handle a surge in online demand and remote working.
Businesses transitioning to cloud computing are speeding the change that will pave the way for future development. Those left behind ponder, “Why did we wait?”
The following are the advantages of moving to the cloud:
- Enhanced flexibility and agility
- Capacity to create more quickly
- Decrease in the requirement for resources
- Improved customer expectations management
- Lowering expenses
- Generate quick business outcomes
- Streamline IT
- Change everything to a service.
- Better control of consumption
- Scalability of clouds
- Enhanced efficiency
Conclusion
A cloud migration strategy necessitates meticulous preparation, testing, and resource allocation. When a cloud migration process begins, the risks are considerable. Both the business and the operations must be secure from the start. A strong cloud migration strategy must guarantee that this component is addressed and that the firm employs cutting-edge cloud technology to stay ahead.
Read More:

